Introduction
Diabetes affects every part of your body, particularly your feet, in addition to your blood sugar. Purpose of foot care As a physician, I have witnessed firsthand how minor foot issues can escalate into major issues if left untreated. In order to prevent serious infections and even amputations, diabetic patients must take proper care of their feet.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Effect on Feet
Blood vessels and nerves are gradually harmed when blood sugar levels stay high. Diabetic patients are particularly vulnerable to foot problems because of poor circulation and nerve damage (neuropathy).
How Diabetes Affects Blood Circulation
Your feet receive less oxygen and nutrients due to reduced blood flow, which slows the healing process. If circulation is compromised, even a small cut could turn into a serious wound.
Nerve Damage (Neuropathy)
Sensation loss results from nerve damage. Blisters, cuts, or pain may go unnoticed by patients, and they may worsen without them realizing it.
Increased Risk of Infection
Patients with diabetes are more susceptible to infections due to weakened immune systems and delayed healing. They could result in gangrene or amputation if untreated.
Why Foot Care Is Vital for Diabetic Patients
Maintaining your independence and avoiding disability are the goals of foot care, which goes beyond simply keeping your feet clean. With the right care, you can:
- Cut down on the likelihood of infections
- Avoid gangrene and ulcers
- Preserve your equilibrium and comfort when walking
- Reduced rates of hospitalization
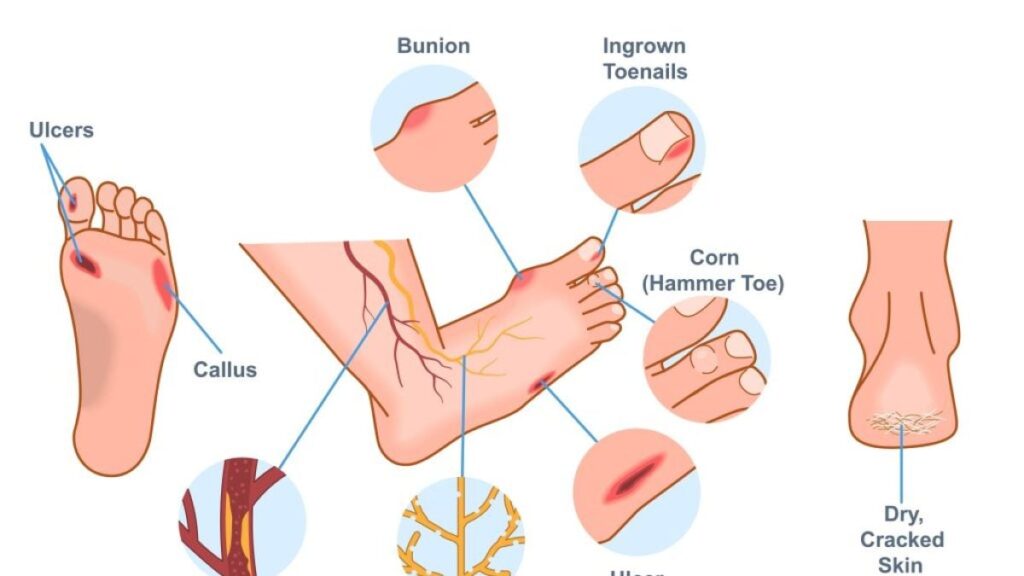
Common Foot Problems in Diabetic Patients
Diabetic Neuropathy
nerve damage that causes loss of feeling; patients may not be aware of injuries.
Foot Ulcers
open sores brought on by friction, pressure, or invisible wounds. These need to be treated right away because they are dangerous.
Poor Circulation
Healing becomes sluggish and challenging in the absence of adequate blood flow.
Fungal Infections and Cracked Skin
Fungal infections and dry skin are frequent, which can cause more problems.
Early Warning Signs to Watch For
Watch out for these warning signs:
- Tingling or numbness
- Skin or nail discoloration
- Chronic edema
- Sores or pain that doesn’t go away
- Bad smell coming from the foot
The Doctor’s Role in Diabetic Foot Care
In terms of education and prevention, doctors are essential.
- Make regular foot assessments.
- Early detection of high-risk areas
- Teach patients how to take care of their feet at home.
- Treat wounds and infections.
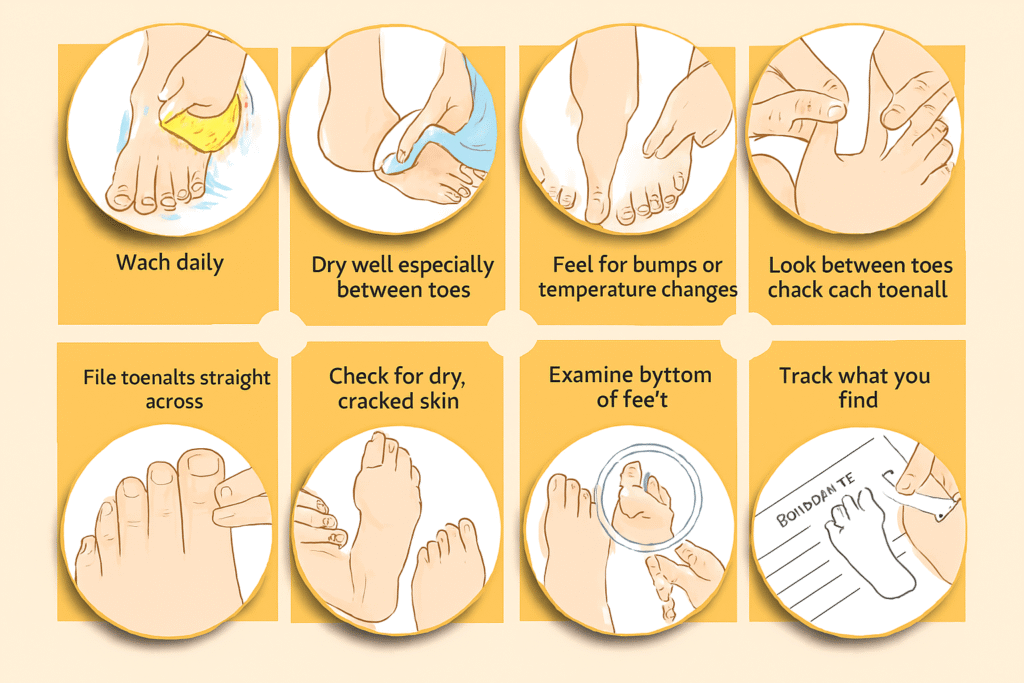
Daily Foot Care Routine for Diabetic Patients
Adhere to this easy, doctor-recommended daily schedule:
- Check your feet every day for cuts, blisters, or swelling.
- Use mild soap and lukewarm water to gently wash your feet.
- Dry completely, paying particular attention to the spaces between toes.
- Use a non-greasy lotion to moisturize.
- Carefully trim your nails so they are straight across rather than curved.
- Put on cozy shoes and fresh, cotton socks.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
See your doctor on a regular basis, even if your feet appear to be in good condition. Regular examinations assist in identifying:
- Problems with circulation
- Damage to the nerves
- Infections of the skin or nails
Preventive examinations save lives and feet.
Proper Footwear and Support
The purpose of diabetic socks and shoes is to lessen friction and pressure.
- Select shoes with soft insoles that are wide and cushioned.
- Steer clear of shoes that are too tight or pointed.
- Put on breathable, seamless socks to ward off moisture.
Managing Wounds and Infections
If a cut or blister is discovered:
- Use saline or a mild antiseptic to gently clean.
- Put on a sterile dressing.
- Don’t go barefoot.
- If it doesn’t go away in a few days, see your doctor right away.
For complex wounds, doctors may suggest advanced wound therapies such as:
- Topical oxygen treatment
- Debridement, or the removal of dead tissue
- Offloading (lessening the strain on the injury)
Preventing Complications
Prevention is the key to managing diabetic foot issues:
- Control your blood sugar levels.
- Quit smoking to increase blood flow.
- Steer clear of extremely hot or cold temperatures.
- Never go barefoot.
- Keep your body weight in check.
Advanced Treatments for Diabetic Foot
Physicians employ cutting-edge techniques such as:
- Topical oxygen therapy: increases the oxygen supply, which hastens the healing process.
- Offloading devices: preventing pressure on wounds
- Compression therapy: increases the flow of blood in the legs.
Psychological and Emotional Support
It can be stressful to have diabetes. Patients frequently experience anxiety related to foot ulcers or amputations. Education and encouragement aid in their confidence recovery. Maintaining daily foot care practices is greatly aided by family support.
Doctor’s Tips for Long-Term Foot Health
- Every night, check your feet.
- Make an appointment for yearly foot exams.
- Keep your nails neat and short.
- Every day, moisturize.
- Replace your worn-out shoes.
- If you notice blisters or wounds, take quick action.
Conclusion
Preventive, protective, and preservation are the goals of diabetic foot care. In order to prevent complications, it is our duty as physicians to inform patients and guarantee prompt treatment. Patients with diabetes can live pain-free, walk with confidence, and avoid major foot issues with proper care.
FAQS
1. Why is diabetic foot care so crucial?
Due to diabetes’s effects on nerves and blood flow, feet are more susceptible to ulcers and infections.
2. How frequently should people with diabetes visit a podiatrist?
At least every six to twelve months, or more frequently if issues are already present.
3. Is it possible to reverse diabetic foot issues?
Although early nerve damage cannot be completely repaired, its progression can be slowed and its symptoms controlled.
4. What are the best shoes for people with diabetes?
Diabetics can wear wide, soft shoes that are cushioned and free of pressure points and tight seams.
5. How can I avoid developing foot ulcers at home?
Wear appropriate footwear, check your feet every day, keep them dry and clean, and monitor your blood sugar levels.


