Introduction to Diabetic Foot Ulcers
A diabetic foot ulcer is one of the most serious complications of diabetes. It develops due to nerve damage, poor circulation, and delayed wound healing.Nursing Care Plan for Diabetic Foot Ulcer If left untreated, it can lead to infection, amputation, and reduced quality of life. A well-structured nursing care plan is essential for promoting healing and preventing complications.
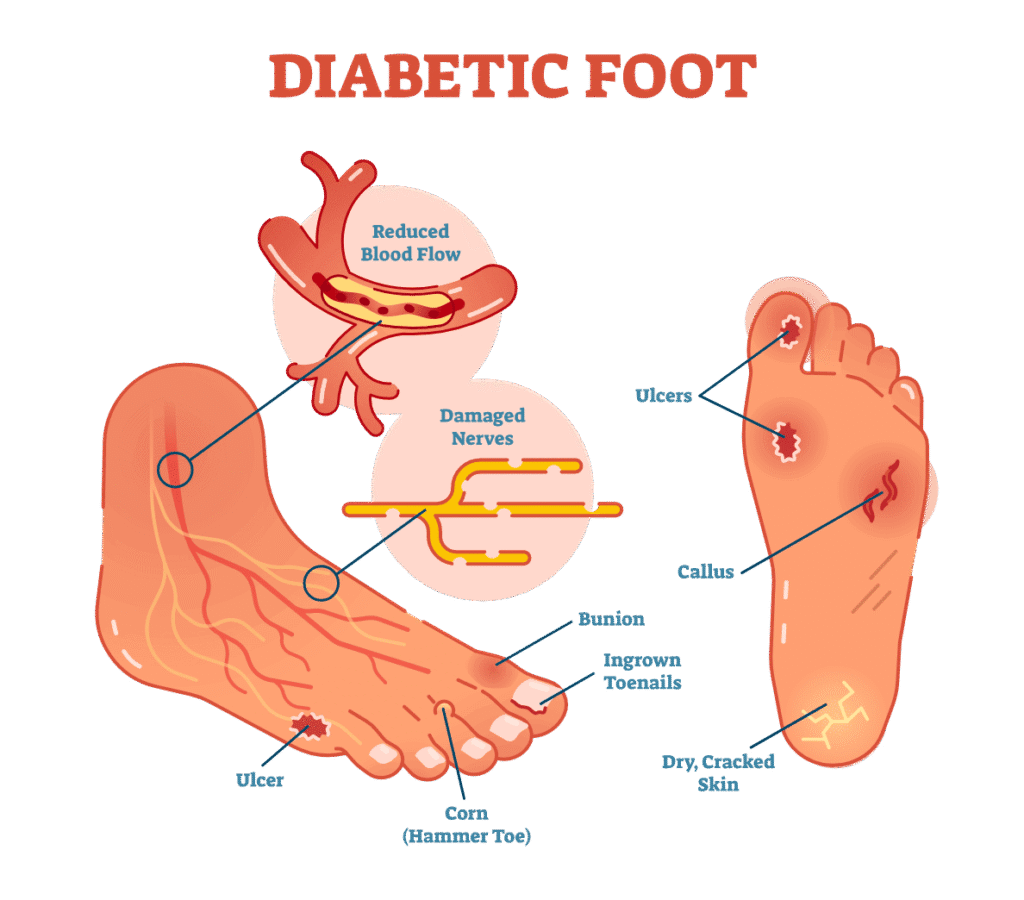
Assessment in Nursing Care Plan
A nursing care plan guarantees long-term healing and efficient control of diabetic foot ulcers. Nurses assist patients in leading better lives by emphasising education, pain management, interventions, and assessment. The cornerstones of diabetic foot health continue to be preventive care and routine checkups.
An Overview of Foot Ulcers in Diabetics
One of diabetes’s most dangerous side effects is a diabetic foot ulcer. Delays in wound healing, inadequate circulation, and nerve injury are the causes of its development. Amputation, infection, and a lower quality of life are possible outcomes if treatment is not received. An organised nursing care plan is necessary to encourage recovery and avoid problems.
Nursing Care Plan Assessment
The first step in treating diabetic foot ulcers is assessment. Nurses should examine the patient’s foot health, blood sugar levels, and medical history. Frequent observation facilitates the early detection of infection and poor wound healing. It’s also critical to identify risk factors, including obesity, smoking, and neuropathy.
Diagnosis of Diabetic Foot Ulcer in Nursing
Several nursing diagnoses apply to diabetic foot ulcers. These include:
- compromised skin integrity as a result of inadequate circulation.
- infection risk as a result of an open wound.
- acute discomfort brought on by ulceration.
- lack of knowledge about wound care and self-care.
Nursing Care Planning
Planning focuses on setting achievable goals. The main objectives are wound healing, infection prevention, pain reduction, and patient education. Nurses should collaborate with doctors, dietitians, and podiatrists to create a holistic care strategy.
Techniques to Treat Diabetic Foot Ulcers
The main component of the nursing care plan is interventions. They include:
- Using sterile methods, clean and treat the wound.
- keeping an eye out for redness, swelling, or an unpleasant smell.
- regulating blood sugar levels with food and medicine.
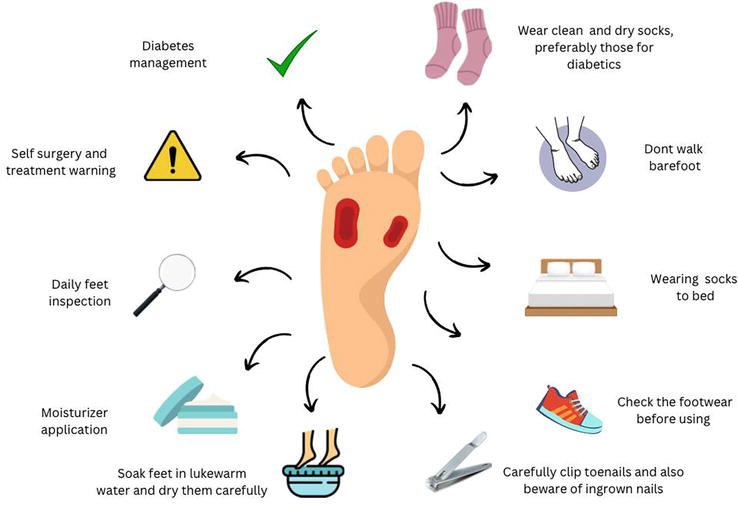
- Instructing patients on daily foot inspection and hygiene
- encouraging the wearing of appropriate footwear to prevent pressure injuries.
Techniques for Pain Management
Diabetic foot sores frequently cause discomfort. Nurses can assist by teaching relaxing techniques, employing unloading devices, and giving prescription painkillers. Regular pain assessments are necessary to modify therapy regimens.
Infection Control Measures
Preventing infection is vital. Nurses are required to use sterile dressings, practise good hand hygiene, and motivate patients to finish their antibiotic treatment. Patients can avoid serious problems if infection indications are identified early.
The Function of Nutrition in Healing
A key factor in wound healing is nutrition. Nurses should advise patients to take vitamins, minerals, and foods high in protein. Additionally, hydration is necessary for a quicker recovery. Patients can receive individualised food programs from dietitians.
Education for Patients and Self-Care
The key to preventing recurrence is education. Blood sugar monitoring, lifestyle modifications, and appropriate foot care should be taught to patients. By teaching kids to examine their feet every day, the likelihood of undetected injury is decreased.
Anticipated Results of the Nursing Care Plan
With proper care, patients can expect improved wound healing, reduced infection risk, and better quality of life. Increased patient knowledge and adherence to treatment are signs of a successful nursing care plan.
Conclusion
A nursing care plan guarantees long-term healing and efficient control of diabetic foot ulcers. Nurses assist patients in leading better lives by emphasising education, pain management, interventions, and assessment. The cornerstones of diabetic foot health continue to be preventive care and routine checkups.


